What Is a Hybrid Solar System? Complete Guide for 2025
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. This post contains affiliate links.
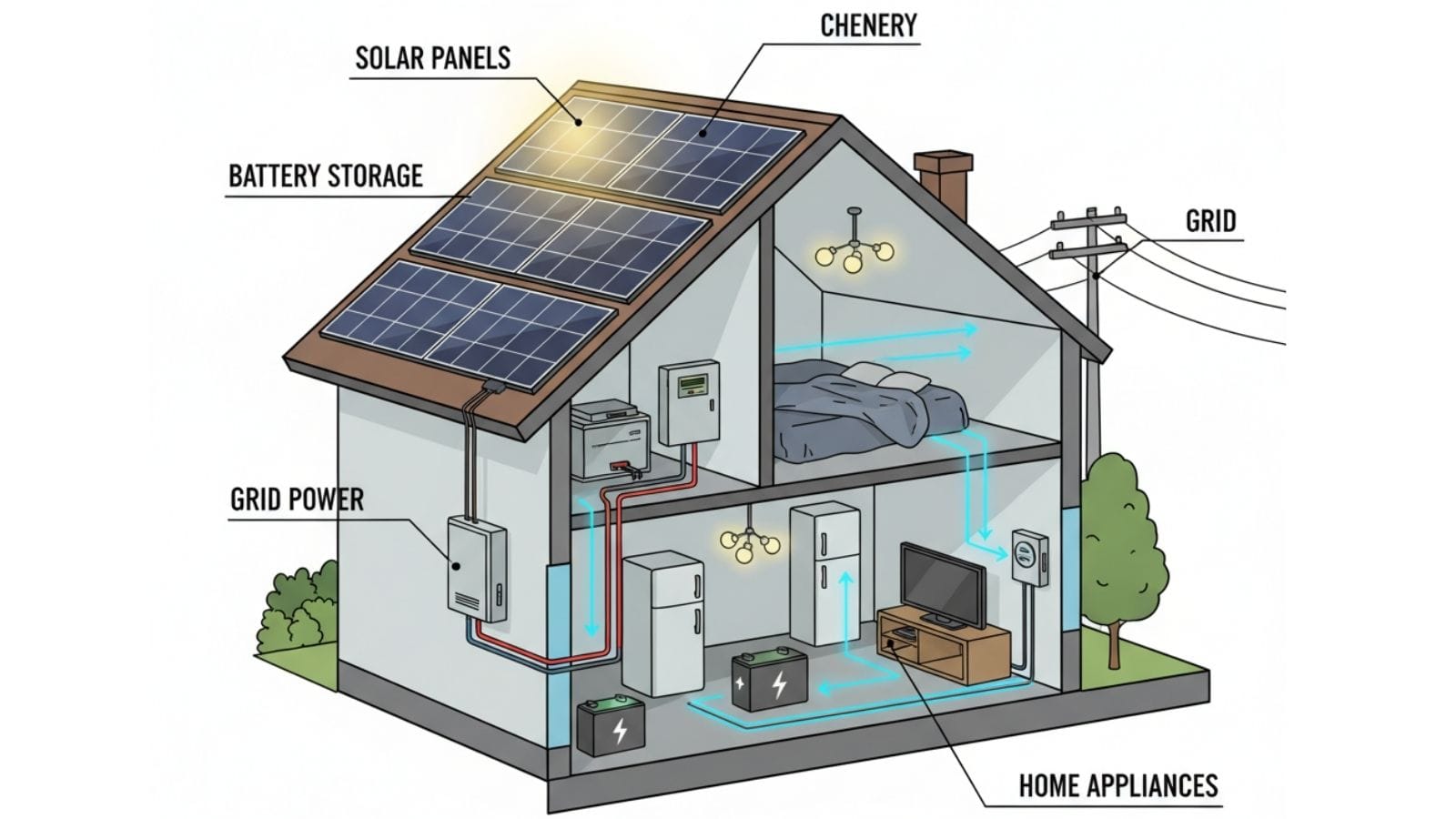
A hybrid solar system is a setup that combines three main components: solar panels, a battery storage system, and a connection to the electrical grid. It’s often called a “hybrid” because it blends the energy independence of an off-grid system with the reliability of a grid-tied system.
During the day, the solar panels generate electricity to power your home. Any excess energy is used to charge your battery bank. At night, or during peak-demand hours, your home draws power from the stored battery energy instead of the grid.
If the battery runs low, the system seamlessly pulls power from the grid as a backup. This guide will explain the technical components that make this possible, how it works in different scenarios, and its key differences from on-grid and off-grid systems.
How a Hybrid Solar System Works
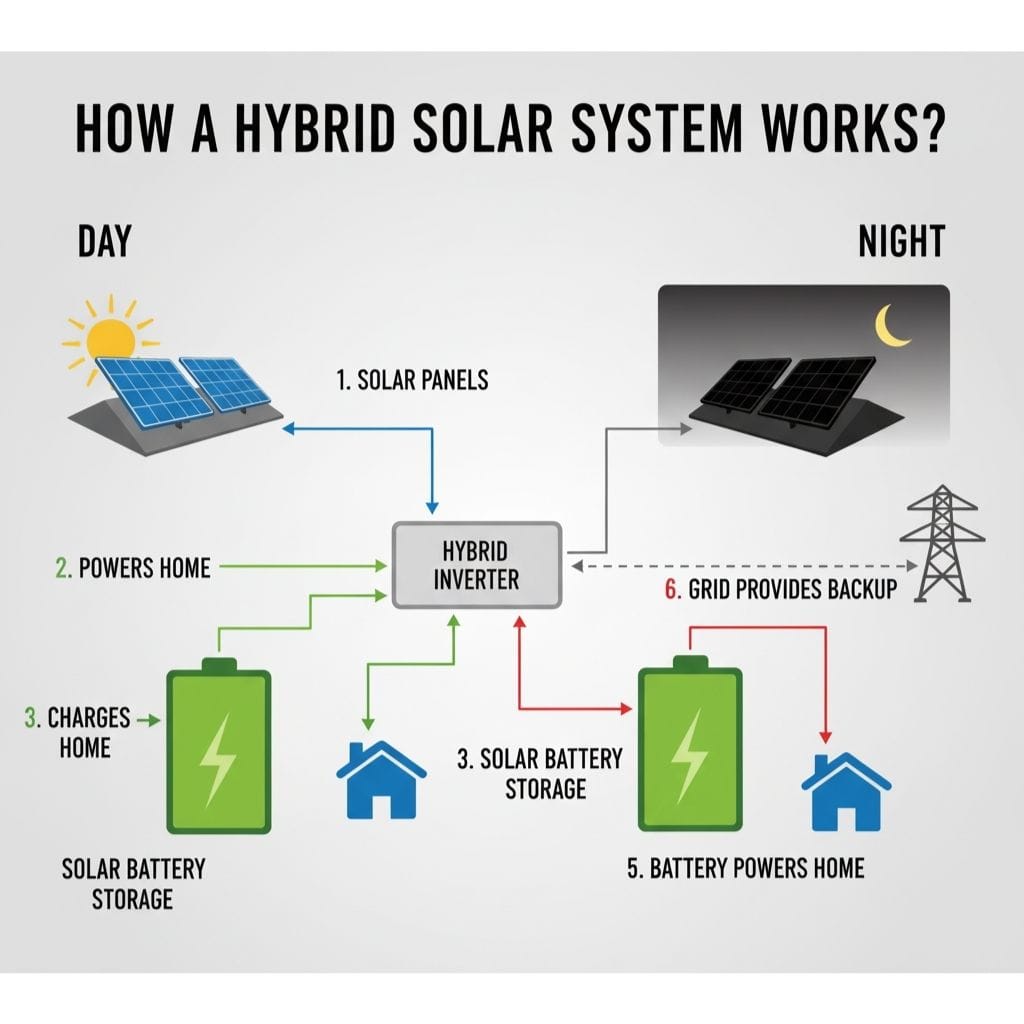
At its core, a hybrid system is an intelligent network that manages the flow of electricity between three main components: your solar panels, a battery storage unit, and the utility grid.
- Generation (The Panels): Your photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight into Direct Current (DC) electricity.
- Conversion (The Hybrid Inverter): This is the “brain” of the system. A hybrid inverter takes the DC power from the panels and makes a series of smart decisions:
- Immediate Use: The first priority is to send power to your home’s appliances. This happens in real time, so you’re using clean solar energy as it’s being produced.
- Battery Charging: Any excess electricity not immediately used is intelligently redirected to your battery storage unit, charging it for later use.
- Grid Export: If your batteries are full and your home’s energy needs are met, the remaining surplus power is sent to the utility grid. In regions with net metering policies, this surplus energy earns you valuable credits that can be used later.
- The Backup (The Battery): When the sun goes down or during a power outage, the hybrid inverter automatically draws power from your battery, ensuring your home remains powered.
- Grid Integration: When your battery reserves are low, the system seamlessly pulls power from the utility grid to keep your home running. This “dual functionality” is what makes a hybrid system so reliable.
This seamless, automated process gives you the ultimate control over your energy consumption, allowing you to use your own power when it’s most valuable and rely on the grid only when absolutely necessary.
Reference: U.S. Department of Energy — Solar Integration: Inverters and Grid Services Basics
For an in-depth look at how solar panels can be connected in series or parallel for optimal performance, read our detailed guide on solar panel wiring basics.
Key Components of a Hybrid Solar System
A hybrid system’s performance depends on how its main components work together. Here are the four key pieces of hardware that make up a complete system:
1. The Right Panels: The Energy Source
While any solar panel will work, the most common and effective choice for a hybrid system is high-efficiency monocrystalline panels. These panels use a single silicon crystal, which makes them more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity. A premium panel will also have a low temperature coefficient, ensuring it performs better in hot weather, and a robust warranty that guarantees a high power output for decades.
2. The Hybrid Inverter: The Brains of the System
The hybrid inverter is what sets this system apart. It is a single, integrated unit that manages the entire energy flow. When choosing a hybrid inverter, you should consider:
- Solar-to-Battery-to-Grid Management: A good hybrid inverter can intelligently prioritize where the energy goes. It will first power your home, then charge your batteries, and finally send any excess to the grid.
- Backup Power Capabilities: The inverter must be able to seamlessly switch to battery power during a grid outage. You should confirm the inverter can handle the full load of your critical appliances.
- Scalability: Look for an inverter that can support future system expansions, such as adding more panels or a second battery.
Best Hybrid Inverter for DIY:
For a reliable hybrid setup, you need an inverter that can handle both grid power and battery charging seamlessly. We recommend the Renogy 48V 3000W Solar Inverter Charger. It acts as a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply), switching to battery power instantly when the grid fails. [Check Price on Amazon]
3. The Battery: The Power Bank
Top Choice for Storage:
To store excess energy for nighttime use, Lithium-Iron-Phosphate (LiFePO4) is the gold standard. The LiTime 12V 100Ah LiFePO4 Battery offers 10+ years of life and is perfect for building a scalable battery bank. [Check Price on Amazon]
Lithium-ion batteries are the most popular choice for home energy storage for a few key reasons:
- High Energy Density: They can store a large amount of power in a relatively small and lightweight package.
- Deep Cycling: They can be discharged and recharged deeply thousands of times without significant capacity loss.
- Long Cycle Life: They have a lifespan of 10–15 years or more, providing long-term value.
4. The Monitoring System: The Eyes and Ears
A robust monitoring system is essential for a hybrid setup. This software tracks your energy production in real time and shows you how much power is being consumed, stored, and sent back to the grid. By monitoring your system, you can ensure it is always performing optimally and spot any issues early on, ensuring long-term performance and reliability.
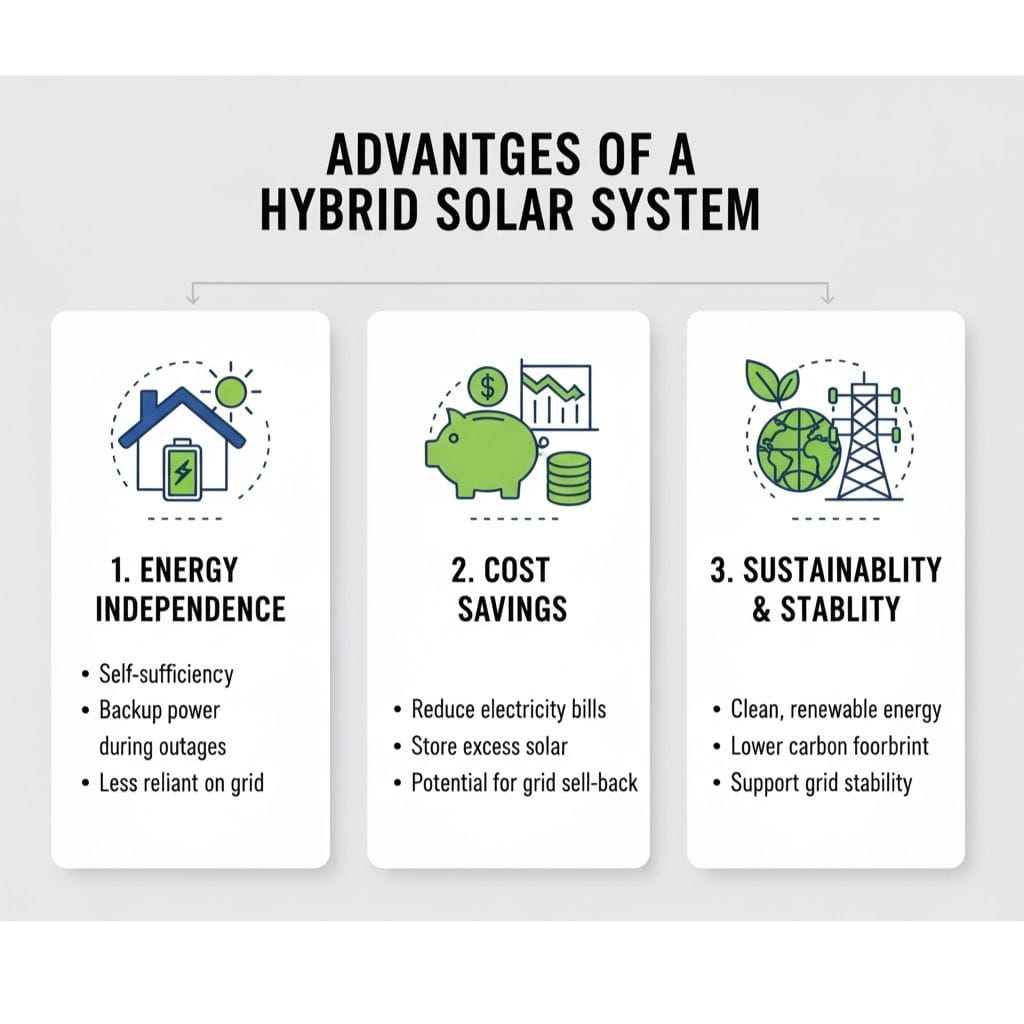
Advantages of a Hybrid Solar System
By combining panels, a battery, and a grid connection, a hybrid system provides three unique categories of benefits over other solar setups:
1. Energy Security and Peace of Mind
A primary benefit is providing backup power and energy security. Unlike a standard grid-tied solar system, a hybrid system with a battery can provide backup power during a grid outage. The transition from grid power to battery power is virtually seamless, ensuring that your home’s critical loads—like your refrigerator, lights, and WiFi—remain powered, even during an extended blackout. This level of energy independence protects you from unpredictable grid failures and provides security for your family.
2. Optimized Energy Usage and Cost Savings
A hybrid system allows for advanced energy management to reduce costs. This is especially valuable for homeowners in regions with Time-of-Use (TOU) electricity rates, where power is more expensive during peak evening hours.
- Demand Management: During the day, your panels charge your battery. In the evening, when grid electricity prices spike, your home automatically uses the stored solar power, effectively “shaving” your electricity consumption during the most expensive hours.
- Peak Shaving: By drawing from your battery instead of the grid, you reduce your reliance on utility power when demand is highest, leading to significant savings on your monthly bill.
3. Financial Return and Grid Support
Grid Resilience: By managing your own energy consumption and contributing to the grid when needed, your hybrid system helps reduce the strain on the local power infrastructure, making the entire community’s energy system more resilient.
Net Metering: In many regions, your utility company will credit you for the excess energy your system sends back to the grid. While a hybrid system prioritizes storing power for your own use, it can still export surplus energy, providing a financial return on the electricity you don’t use.
Limitations and Considerations
While they offer many advantages, hybrid systems also have specific trade-offs, costs, and requirements to be aware of:
1. The Financial Reality: Higher Initial Cost
The most significant limitation of a hybrid system is its higher upfront cost. On average, adding battery storage can increase the total system price by 20% to 40% compared to a standard grid-tied solar setup. The battery itself is often the most expensive component of a hybrid system, and its cost is a major factor that must be weighed against your specific energy goals and financial situation. For homeowners whose primary goal is simply to reduce their monthly electricity bill, a grid-tied system is often the most cost-effective solution.
2. Maintenance and Long-Term Costs
While solar panels themselves are low-maintenance, the battery and inverter in a hybrid system require more attention over their lifespan.
- Battery Replacement: Solar batteries, even high-quality lithium-ion models, have a finite lifespan, typically 10 to 15 years. They will need to be replaced, which adds a significant long-term cost to the system.
- Periodic Servicing: To maintain optimal performance, batteries and inverters should be inspected periodically by a qualified professional. This ensures the system is operating safely and at peak efficiency, and helps identify potential issues before they become expensive problems.
3. Space and Installation Requirements
A hybrid system requires more space than a simple grid-tied setup. The battery bank and additional components need a dedicated, well-ventilated space that is protected from extreme temperatures. Many homeowners choose to install them in a garage, basement, or utility room. This added hardware and complexity can also lead to a longer and more complex installation process.
For insights on how solar panels perform in different weather conditions, including snow, rain, and extreme heat, check our in-depth weather performance guide.
Common Misconceptions About Hybrid Solar Systems
Misunderstandings about hybrid solar systems can lead to unrealistic expectations about their performance and capabilities. A professional analysis of these systems requires looking beyond the marketing and understanding the technical realities. Let’s address some of the most common misconceptions.
Misconception 1: “Hybrid systems operate completely off-grid.”
Truth: While a hybrid system can provide a homeowner with the power to operate independently during an outage, it is, by definition, a grid-tied system. It remains connected to the utility grid for two crucial reasons:
- Energy Security: The grid provides a reliable source of supplemental power. When your solar panels aren’t producing and your batteries are depleted—during a long stretch of cloudy days, for example—your system will seamlessly draw power from the grid to keep your home running.
- Financial Return: Being connected to the grid allows you to sell any excess energy back to the utility, providing a financial return through net metering. A true off-grid system has no connection to the grid and, therefore, cannot take advantage of these savings.
Misconception 2: “All hybrid systems are eligible for net metering.”
Truth: This is one of the most important factors to verify. Net metering policies are determined by local utility companies and state or federal regulations, not the system itself. Many regions have strong net metering programs, but others have policies that are less favorable, such as a lower credit rate for exported energy. Before choosing a hybrid system with the goal of selling power back, you must confirm the specific policies that apply to your home.
Misconception 3: “Battery storage lasts forever.”
Truth: Even the highest-quality batteries have a finite lifespan. Modern lithium-ion batteries are built for longevity, with a typical useful life of 10 to 15 years. Over time, they experience a gradual loss of capacity, meaning they can hold less and less charge. Just like the battery in your phone or electric car, they will eventually need to be replaced. This is a significant long-term cost that must be factored into your long-term budget.
How Is a Hybrid Solar System Sized?

Designing a hybrid solar system is a meticulous process that goes far beyond simply estimating your monthly bill. For a system to provide optimal performance, it must be carefully sized to meet your unique energy consumption habits and long-term goals. This is a task for a professional, and here’s how they approach it with precision.
The Sizing Process: A Professional’s Approach
A skilled installer treats solar system sizing like a science. Instead of relying on guesswork, they use a data-driven approach to ensure your system is perfectly tailored to your needs.
- Analyze Your Energy Profile: The first and most critical step is to understand your energy consumption. A professional will ask to see your utility bills from the last 12 months. This full-year data provides a clear picture of your average daily and monthly usage (in kWh), and, just as importantly, highlights seasonal variations. For example, your energy needs in a hot summer month with heavy air conditioning use will be far greater than in a mild spring.
- Estimate Your Peak Load: This is where a professional’s expertise is invaluable. They will not only look at your total consumption but also identify your peak load—the maximum amount of power your home draws at any single moment. This is crucial for sizing the inverter and batteries. If you have a peak load of 7 kW (from running your AC, oven, and washer all at once), your inverter and battery must be capable of handling that power, even for a short time.
- Model Your System with Software: Professional installers use advanced software tools like Aurora Solar or Helioscope. These programs use your home’s unique data—including its roof orientation, shading from nearby trees or buildings, and local solar irradiation data—to create a precise 3D model of your potential system. This allows them to simulate performance across all seasons and provide an accurate projection of your expected energy production.
- Calculate Battery Needs for Your Lifestyle: With your energy consumption and peak load in hand, your installer will calculate the right amount of battery storage to meet your specific needs. Do you want to power only your “critical loads” (e.g., refrigerator, lights, Wi-Fi) for a single day? Or do you want a full-home backup for multiple days? The answer to this question is a major factor in determining your battery bank size and overall system cost.
By following these professional steps, an installer ensures your hybrid system is accurately sized to provide reliable power and long-term performance.
Portable Hybrid Solution:
Want the benefits of a hybrid system without the complex installation? The EcoFlow DELTA Pro Ultra can connect to your home circuit (via a Smart Home Panel) to provide backup power and lower your bills, acting as a plug-and-play hybrid system. [Check Price on Amazon]
Typical Costs of a Hybrid Solar System
When evaluating a hybrid solar system, the initial cost is a significant factor. It’s helpful to understand what components make up the total price. Here is a general breakdown of what drives the cost of a typical professional installation.
The Breakdown: What Drives the Cost?
The price of a hybrid solar system can vary widely, but a typical residential system of 5–10 kW generally falls within the $22,000 to $42,000 range before incentives. This cost is determined by several key components:
- Solar Panels: The number and efficiency of your panels are a primary factor. Premium, high-efficiency panels will have a higher cost per watt but can generate more electricity in a smaller space.
- Hybrid Inverter: The “brain” of the system can cost $2,000 to $4,000 on its own, depending on its capacity and smart features.
- Battery Storage: This is the single most expensive component, often costing $10,000 to $20,000 or more depending on its capacity and chemistry.
- Labor & Soft Costs: Permitting, installation, and overhead can make up a significant portion of the total price.
Maintenance Best Practices
Solar panels are remarkably durable, but a hybrid system’s battery and inverter require regular attention to ensure consistent performance and longevity. Maintenance is divided into two parts: tasks for the homeowner and tasks for a professional.
1. Homeowner Maintenance: The Eyes and Ears
As a homeowner, your most important job is to be the first line of defense for your system.
- Quarterly Visual Inspections: Get into the habit of visually inspecting your panels every three months from the ground. Look for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks, chips, or discoloration. Check for debris, like leaves or bird droppings, that may be accumulating. A quick rinse with a garden hose on a cool, overcast day is often all that’s needed to keep them clean.
- Regular Monitoring: Your system’s monitoring software is your most powerful tool. Check it regularly—ideally every few days—to ensure your energy production is following a predictable curve. A sudden or gradual drop in output on a sunny day could be an early warning sign of a problem, such as a dirty panel, a shading issue, or a hardware fault.
- Check Battery Health: Your monitoring app will also provide key information about your battery’s health, including its state of charge (SOC) and historical performance. This allows you to track its performance over time and ensures it is charging and discharging as expected.
2. Professional Care: The Expert Touch
A professional inspection is critical for your system’s longevity.
- Annual System Inspection: A certified technician should perform a comprehensive inspection at least once a year. This goes beyond what you can see from the ground. The technician will:
- Test all electrical connections to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion.
- Verify the inverter’s performance and check for any error codes.
- Inspect the mounting hardware to ensure it is stable and secure against wind and weather.
- Firmware Updates: Modern inverters rely on embedded software to operate efficiently. A technician can ensure your inverter’s firmware is up-to-date. These updates often include performance optimizations, bug fixes, and enhanced compatibility with new devices, which is essential for a smart, long-lasting system.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hybrid Systems
Do hybrid solar batteries need to be replaced
Yes, solar batteries have a finite lifespan and will eventually need to be replaced. The most popular batteries for hybrid systems are lithium-ion, which typically last 10 to 15 years. This lifespan depends on how often the battery is used (its “cycle life”) and the temperature of its environment. Over time, all batteries experience a gradual loss of capacity, meaning they can hold less and less charge. This is a significant long-term cost that you should factor into your long-term budget
Can I expand my hybrid solar system in the future?
In most cases, yes, a hybrid solar system can be expanded, but it depends on your initial setup. The most critical component for future expansion is the inverter. If you anticipate adding more panels or a second battery in the future, it’s wise to install a slightly larger inverter than you need for your current setup. This provides the capacity to handle increased solar input without needing a full system overhaul. Additionally, you must consider local utility regulations, as some regions have limits on the total system size a homeowner can install.
Is cleaning the solar panels necessary?
Yes, periodic cleaning is essential for maintaining a high level of performance. While rainwater helps rinse away some dirt, dust, pollen, and other debris can accumulate on your panels and create a layer that blocks sunlight. This can lead to a significant drop in efficiency. Industry studies show that a clean solar panel can generate 5-10% more power than a dirty one. The frequency of cleaning depends on your location. Panels in dusty or polluted areas (like near a busy road or in a desert) may need to be cleaned more often than those in a rainy climate.
Will my hybrid system work during a power outage?
Yes, a major benefit of a hybrid system is its ability to work during a power outage. When the grid goes down, the hybrid inverter automatically disconnects from the utility and transitions to “islanding” mode. It will then draw power from your battery to keep your home’s essential appliances running. The duration of your backup power depends on the size of your battery and how much energy you are using. For example, a single battery may only be able to power critical loads like your refrigerator and a few lights for a day, while a larger battery bank can provide whole-home backup for multiple days.
You have now reached the end of this guide. We have explored the technical components, real-world benefits, and practical considerations of a hybrid solar system. Ultimately, the decision to invest in this technology is a highly personal one that hinges on your specific energy goals and financial situation.
Is a Hybrid Solar System the Right Choice for You?
A hybrid solar system offers a powerful blend of energy independence and grid reliability, combining battery storage with a grid-tied setup. As this guide has shown, it provides backup power and advanced energy management, but it also has a higher initial cost and more complex components than a simple grid-tied system.
Understanding the core technology—from its components and limitations to its maintenance needs—is the first step. For a detailed analysis of your specific home and energy goals, we recommend consulting with a certified solar professional.

Solar Energy Enthusiast & Renewable Energy Researcher
Vural’s journey into solar energy began four years ago, driven by frequent power outages and high electricity bills at his own home. He has since gained hands-on experience with both personal and commercial solar projects. At solarpanelresource.com, Vural shares his real-world insights and in-depth research to guide homeowners and business owners on their own path to energy independence.