Future of Solar Energy: Trends to Watch in 2025 and Beyond
The global energy landscape is undergoing a major transformation, and at the heart of it lies solar power. The future of solar energy is not just about clean electricity generation—it is about technological breakthroughs, smarter grids, sustainable policies, and financial models that make solar accessible for everyone.
As we move toward 2025 and beyond, understanding the direction of solar innovation will empower homeowners, businesses, and policymakers to make better decisions. As a leading voice in renewable energy, I can tell you that the solar industry is entering a new era. The unprecedented growth in 2024, with nearly 600 GW of new capacity added globally, solidified solar’s position as the leading force in the world’s energy transition, accounting for over 80% of all new renewable capacity. This article explores in depth the trends, challenges, and opportunities shaping the future of solar power worldwide, drawing on data from trusted sources like the International Energy Agency (IEA) and SolarPower Europe.
Global Solar Energy Market Outlook for 2025
The solar market is not just growing—it’s experiencing record-breaking, exponential expansion. According to leading industry reports, the market is projected to see a **compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 15% between 2023 and 2030**. This incredible momentum is being led by established markets in Europe, North America, and Asia, which are driving adoption through both massive utility-scale farms and widespread residential rooftop installations.
A key driver of this growth is supportive government policy. Countries around the world are enacting powerful incentives like **tax credits, feed-in tariffs, and net-metering schemes** that make solar energy an easy and smart financial decision for consumers. By the end of 2025, it’s projected that over 30% of new residential buildings in developed countries will be designed to include solar panels as a standard feature, not an afterthought. Pioneers like Germany and Australia are pushing the boundaries with innovative **community solar projects** that enable shared ownership and dramatically reduce energy costs for residents.
This solar revolution isn’t limited to developed nations. Emerging markets in Africa and South America are increasingly turning to solar power to meet energy needs in remote areas where traditional grid infrastructure is either nonexistent or unreliable. With decreasing installation costs and more affordable energy storage systems, solar is poised to become the most cost-effective energy solution globally—a true game-changer for energy access and economic development.
Key Technological Innovations Driving Solar Energy

In 2025, solar technology will not look the same as it did a decade ago. The solar industry is in the midst of a technological revolution, with innovations that are rapidly reshaping what’s possible. These breakthroughs are driving solar’s future far beyond traditional rooftop panels.
One of the most exciting developments is perovskite solar cells. These next-generation cells hold the promise of efficiency rates exceeding 30%. Unlike traditional silicon, perovskites can be manufactured using lower-cost, simpler methods like printing or spraying. Research continues to tackle their stability challenges, but they are already beginning to see commercial use.
Building on that, tandem solar cells are setting new world records. By stacking layers of different materials—for example, a perovskite layer on top of a conventional silicon cell—these cells capture a broader spectrum of sunlight, leading to record-breaking conversion efficiencies. In 2025, the certified efficiency record for a large-area perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell was an astounding 34.85%, a leap that surpasses the theoretical limit of a single silicon cell.
Beyond efficiency, a key innovation is transparent solar panels. This technology is transforming how we think about solar integration. Soon, windows, building facades, and other glass surfaces will not just provide light and insulation but will also generate electricity. These building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) are not only a clean energy source but also a new architectural material, seamlessly blending with urban landscapes.
These innovations show that the future of solar is not limited to traditional rooftops. Imagine vehicles, wearable devices, and even infrastructure like sound barriers and bicycle paths generating their own clean power. The widespread application of these new technologies will make solar energy ubiquitous, transforming every surface into a potential source of clean electricity.cutting-edge solar technology advancements.
The Rise of High-Efficiency Panels and Bifacial Technology
As the global solar market matures, a premium is being placed on maximizing energy output from every available square foot. Space limitations in dense urban areas have pushed manufacturers to relentlessly pursue higher-efficiency designs. Modern monocrystalline solar panels already achieve efficiency levels of **22% or higher**, a significant leap from just a few years ago. But the real game-changer is **bifacial technology**.
Bifacial panels are engineered to generate electricity from both the front and back sides by capturing reflected sunlight from surfaces like rooftops, the ground, or even snow. According to recent field studies by organizations like the **National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL)**, bifacial modules can deliver an additional **5-30% more power** annually than their standard, single-sided counterparts, depending on installation conditions and surface reflectivity.
For large-scale commercial and utility projects, bifacial panels are rapidly becoming the industry standard. Their ability to deliver a higher energy yield per square meter is an essential factor in dense urban environments or on expensive land where maximizing output is critical for a strong return on investment. The future of solar isn’t just about putting panels on a roof; it’s about using every surface to generate the most energy possible.
Integration with Energy Storage Systems
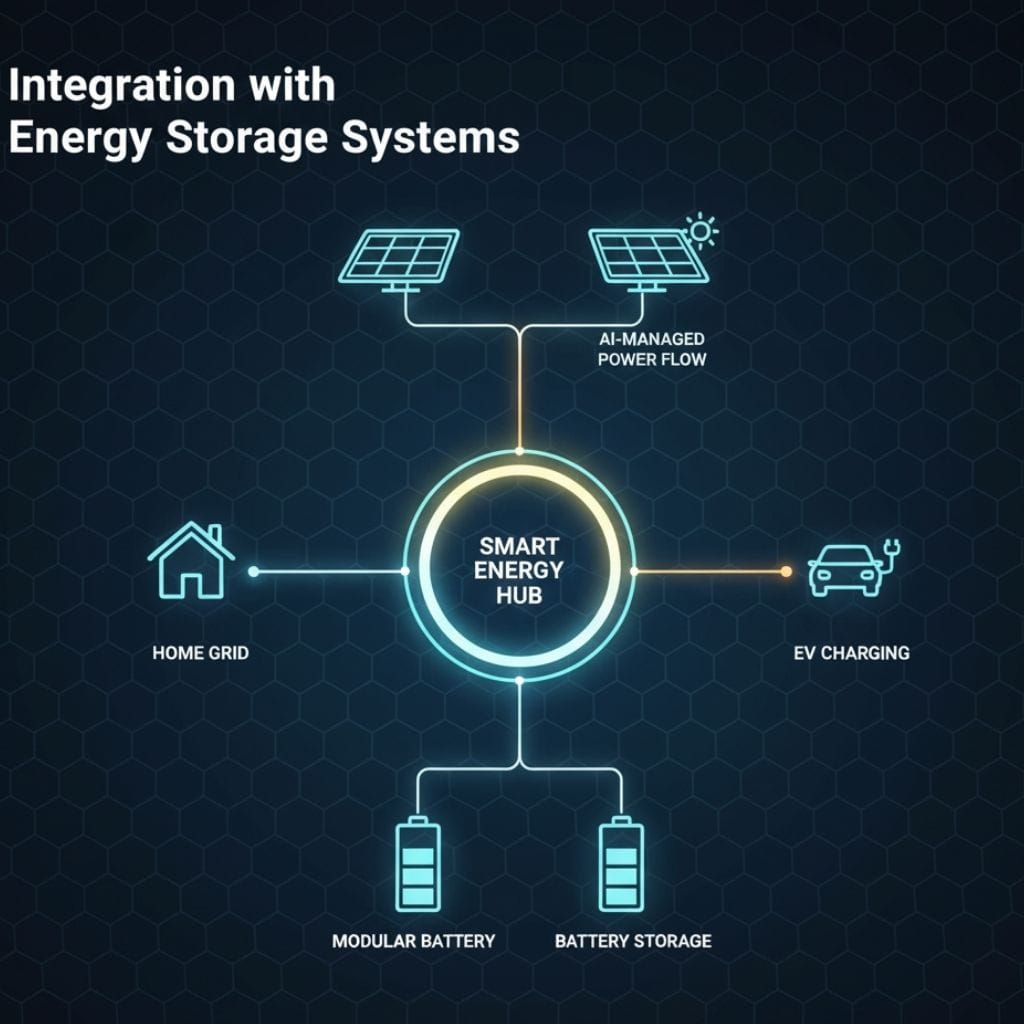
Solar production peaks during the day, but energy consumption often spikes in the evening. This fundamental mismatch between generation and usage is being solved by integrating solar with cutting-edge energy storage solutions.
In 2025, lithium-ion batteries remain the market leader for a reason: their high energy density, efficiency, and dropping costs make them the go-to choice for both residential and commercial applications. However, the future is not limited to a single technology. New solutions, such as solid-state batteries and flow batteries, are emerging rapidly, promising even greater safety, longer lifespans, and suitability for large-scale, long-duration storage.
As a solar energy expert, I can tell you that solar-plus-storage systems are now considered the gold standard for a resilient and financially smart solar investment. These systems allow homeowners to store surplus energy generated during the day and use it during peak demand hours in the evening, when electricity prices are highest. This not only reduces electricity bills but also provides critical backup power during grid outages. For businesses, investing in large-scale battery farms is becoming a standard practice to stabilize their energy supply, reduce reliance on the grid, and hedge against volatile grid prices.
Furthermore, the technology behind these systems is getting smarter. Advanced battery management software, often powered by AI, is now standard. This software optimizes charging and discharging cycles to extend battery life, maximize efficiency, and increase your overall return on investment, turning your solar system into a truly intelligent energy hub.
Smart Grids and AI: How Solar Fits into the Future Grid
The traditional power grid was designed for a one-way flow of electricity from large, centralized power plants to homes and businesses. However, the rise of decentralized energy sources like solar panels is fundamentally changing this model. The solution lies in **smart grids**, which are modernizing the way electricity is distributed. When paired with **artificial intelligence (AI)**, these grids can analyze vast amounts of real-time data from solar installations, weather patterns, and consumption habits. This allows utilities to predict supply and demand more accurately, preventing blackouts and improving overall efficiency.
As a solar and energy expert, I see AI as the “brain” of the new energy system. AI-driven inverters can dynamically adjust energy flow in real-time, for example, by directing surplus solar energy to a battery storage system or feeding it back to the grid when prices are highest. This ensures that every watt generated is used most effectively. According to a recent report from the European Commission, many energy companies are expected to roll out AI-enhanced grid management systems by the end of 2025 that enable a smoother, more reliable transition to renewable-heavy power networks. This intelligent integration ensures that solar energy is not just an alternative power source, but a core component of a resilient and efficient energy future.
Emerging Trends in Solar Financing and Policies

Cost is one of the biggest barriers to solar adoption, but innovative financing is breaking down these walls. The future of solar is not just in technology, but in making it financially accessible to a wider audience.
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), for example, allow property owners to install a solar system with little to no upfront cost. Instead of buying the system, they simply pay for the electricity it produces at a fixed, often lower rate than their utility company. The installer or a third-party developer owns and maintains the system, removing the financial and operational risk from the homeowner. This model is becoming increasingly popular because it allows for immediate energy savings without the significant initial investment.
Additionally, new financing and ownership models are expanding access to solar. Leasing models and community solar projects are giving people in apartments, renters, or those with shaded homes the ability to benefit from renewable energy without a physical installation on their property. This democratizes access to solar energy, ensuring that everyone can participate in the transition to clean power.
Government policies are also adapting to support this growth. Carbon credits and renewable energy certificates provide extra revenue streams for solar system owners, making the investment even more attractive. Looking ahead, experts project that we will see more aggressive climate targets leading to higher subsidies and faster permitting processes, especially in regions committed to net-zero emissions by 2050. These financial and political shifts are what will truly accelerate solar adoption on a global scale.
Sustainability and Recycling: What Happens to Old Panels?
One of the most common concerns about the long-term impact of solar energy is what happens to the panels at the end of their life. As millions of panels installed over the past two decades begin to approach their end-of-life, the focus on recycling and repurposing is no longer just a good idea—it’s a critical part of the industry’s future. The good news is that solar panels are not simply discarded; they are a valuable source of raw materials.
Manufacturers are developing sophisticated systems to recover valuable materials like **silicon, silver, and glass**. This effort is not just about waste management; it’s about building a sustainable, circular economy. By recovering these materials, the industry can reduce waste and significantly lower the environmental footprint of future production. According to the **International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)**, by 2050, the cumulative value of recoverable materials from old solar modules could exceed **$15 billion** globally.
This commitment is being driven by policy. In the European Union, strict **Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)** directives are already in place, requiring solar manufacturers to manage the collection and recycling of their products. Similar policies are being adopted worldwide, turning waste panels into a resource for new installations. Companies investing in these recycling technologies are gaining a significant competitive edge by reducing their material costs and demonstrating a clear commitment to sustainability—a key factor for both investors and environmentally conscious consumers.
Predictions for Solar Adoption in Homes and Businesses

Homeowners are increasingly drawn to solar because it directly addresses two key concerns: reducing monthly energy bills and increasing property value. By 2025, residential rooftop solar is expected to account for over 40% of new installations globally, driven by these clear financial benefits. Many homeowners are also pairing solar panels with smart home systems to track energy production and consumption in real time, turning their homes into intelligent, energy-efficient hubs.
In the commercial sector, the motivation is often tied to meeting ambitious Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals. Corporations, from retail chains to logistics hubs and data centers, are installing large-scale solar arrays to not only reduce operational costs but also to promote a green image to their consumers and investors.
Beyond traditional rooftops, businesses are adopting innovative solutions that help them maximize both land use and energy production. Solar carports, for example, provide clean energy while simultaneously offering shade and protection for vehicles. Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) turn building facades and windows into active power generators. Furthermore, floating solar farms on reservoirs and ponds are a clever way for businesses and municipalities to generate clean energy without taking up valuable land.
Challenges to Overcome for a Solar-Powered Future
Despite the remarkable progress and record-breaking growth, the path to a fully solar-powered future is not without its hurdles. For the industry to truly scale, it must effectively address a number of key challenges. These are the issues that policymakers, investors, and innovators are working on every day to solve.
- Upfront Costs and Financial Hurdles While the cost per watt of solar has plummeted over the last decade, the initial upfront investment for a complete system can still be a significant barrier for many homeowners and businesses. This is especially true in regions without strong government incentives. Addressing this challenge requires continued innovation in financing models, such as **Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)**, and robust policies that make solar financially accessible to a wider demographic.
- Grid Integration and Infrastructure A solar-powered future relies on a grid that can handle a decentralized flow of electricity. Many regions, however, have outdated infrastructure designed for a one-way flow of power from a central plant. Integrating millions of distributed solar systems poses technical issues, including grid instability and voltage fluctuations. Solving this requires massive investment in grid modernization, including the deployment of **smart grid technologies** and advanced energy management systems.
- Intermittency and Weather Dependency Solar energy is, by nature, dependent on the weather. Panels produce peak energy on sunny days and significantly less on cloudy days or at night. This intermittency means solar alone cannot meet a region’s entire energy demand without complementary technologies. The solution lies in building out a resilient energy mix that includes **energy storage systems** (like batteries), robust wind power capacity, and flexible grid management. This ensures a stable and reliable supply of electricity around the clock.
To address these complex challenges, industry stakeholders are collaborating more than ever. They are investing heavily in research and development, training the next generation of skilled solar technicians, and advocating for stronger, more consistent policy frameworks. This close partnership between governments, private investors, and academic institutions will be crucial for accelerating the pace of solar innovation and deployment, ultimately paving the way for a sustainable energy future.
Preparing for the Next Solar Revolution
The future of solar energy is not a distant dream—it is unfolding right now, and its momentum is undeniable. We’ve moved from simple photovoltaic panels to a complex ecosystem of high-efficiency modules, smart energy grids, and powerful storage solutions. From high-efficiency monocrystalline modules to flexible thin-film panels and advanced energy storage, every development brings us closer to a world powered primarily by the sun.
As a solar industry professional, I can assure you that this is more than just a technological shift; it’s an economic and environmental one. By staying informed about the latest trends—from the rise of bifacial panels and perovskite cells to innovative financing models and recycling programs—you can be an active participant in this transition. Keeping an eye on these trends will help you make informed choices, whether you are investing in a new rooftop solar system, managing a commercial facility, or shaping energy policy.
Ultimately, the solar revolution is a collaborative effort. By embracing these innovations, supporting sustainable manufacturing, and advocating for smart policies, we can all contribute to building a more resilient, clean, and efficient energy future. The path forward is bright, powered by limitless sunlight, and it’s here for us to seize.
Key Takeaways: A Look Ahead to Solar’s Future
The journey to a clean energy future is well underway, with solar power leading the charge. Our exploration of the industry’s trajectory reveals a clear path forward, defined by innovation, economic viability, and a strong commitment to sustainability. Here are the most important takeaways you should know about the future of solar.
- Unprecedented Market Growth The global solar market is in the midst of a historic expansion. Fueled by decreasing costs and supportive government policies, this rapid growth is projected to continue well beyond 2025. This makes now an ideal time for homeowners and businesses to invest in solar, taking advantage of a competitive market and powerful incentives.
- Innovation Driving Efficiency and Application The panels of tomorrow are already here. Technological advancements like **perovskite cells** and **bifacial panels** are pushing efficiency to new heights. These innovations are not just improving power output but also expanding solar’s potential beyond traditional rooftops, with applications in windows, vehicles, and even water reservoirs. This means solar will soon be an even more ubiquitous part of our daily lives.
- Reliability Through Integration The days of solar being an intermittent power source are fading. The integration of advanced **energy storage solutions** and **AI-managed grids** is making solar power more reliable and scalable than ever before. These complementary technologies ensure a stable and consistent energy supply, even on cloudy days or at night, creating a more resilient and efficient power network.
- A Sustainable and Accessible Future The solar industry’s commitment to sustainability extends to the end of a panel’s life. With robust **recycling initiatives** and supportive government policies, the industry is creating a circular economy that recovers valuable materials and reduces waste. This focus, combined with innovative financing models, ensures that the future of solar is not only powerful and efficient but also environmentally responsible and financially accessible to everyone.
Click to read our blog post titled “What is a Solar Panel and How Does It Work?
Click to read our article titled Which Solar Panel Should You Choose?

Solar Energy Enthusiast & Renewable Energy Researcher
Vural’s journey into solar energy began four years ago, driven by frequent power outages and high electricity bills at his own home. He has since gained hands-on experience with both personal and commercial solar projects. At solarpanelresource.com, Vural shares his real-world insights and in-depth research to guide homeowners and business owners on their own path to energy independence.







